What Are the Different Antibiotics Used For Gum Disease?
Welcome to our blog, where we dive into the fascinating world of dental health! Today, we’re delving into a topic that might not be on everyone’s radar but is crucial for maintaining a healthy smile: gum disease and antibiotics.
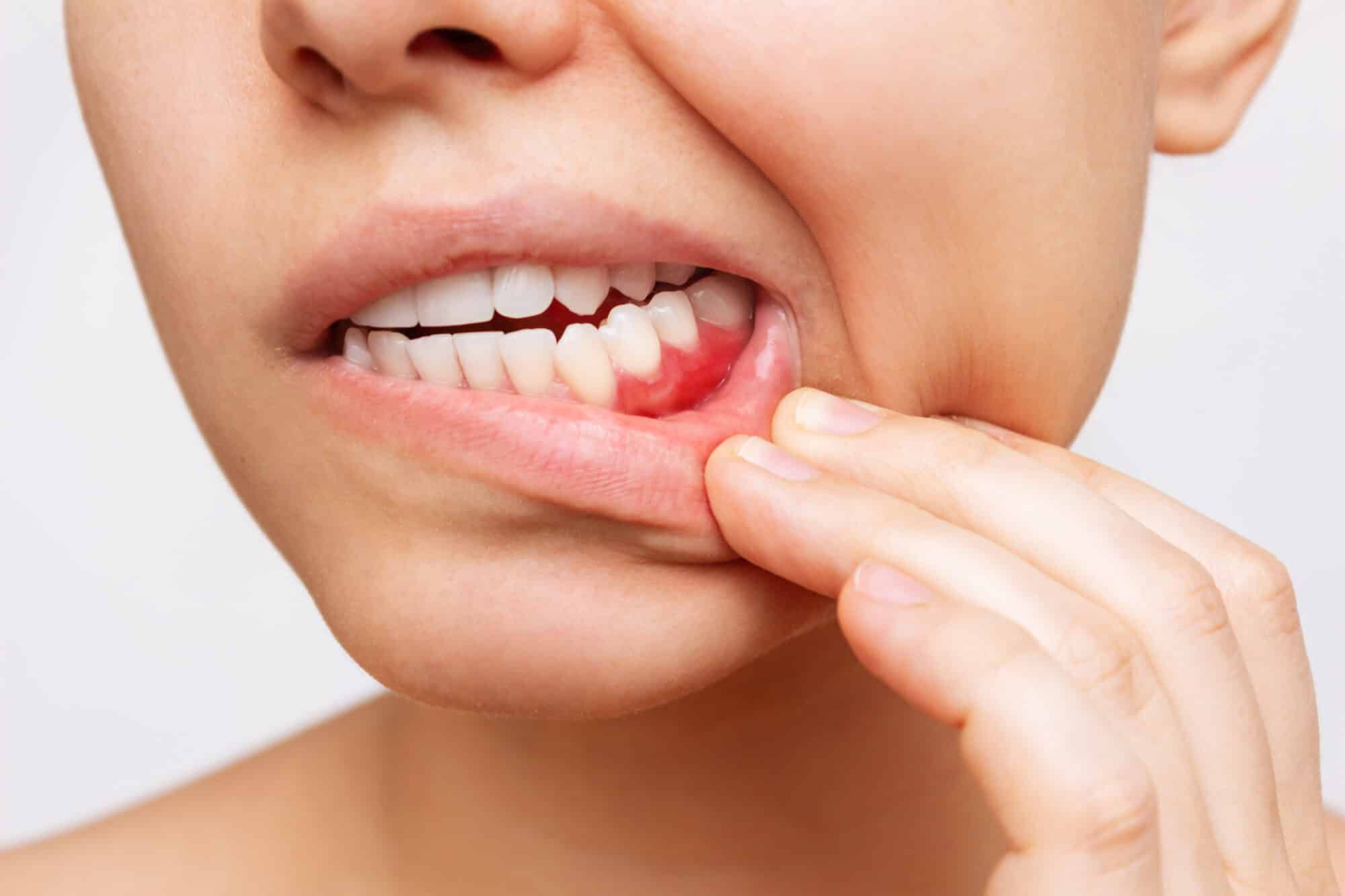
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an all-too-common oral condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It starts with mild symptoms like swollen or bleeding gums but can progress to more serious issues if left untreated. Luckily, there are various treatment options available to combat gum disease, and antibiotics play a significant role in this fight.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of antibiotics used in gum disease treatment and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. We’ll also delve into precautions and side effects associated with antibiotic use for gum disease. And fear not – if you prefer natural alternatives, we’ve got you covered too!
Types of Antibiotics Used in Gum Disease Treatment
When it comes to treating gum disease, antibiotics can play a crucial role in eliminating bacteria and reducing inflammation. Several types of antibiotics are commonly used in the treatment of gum disease.
One common type is tetracycline, which works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. It can be taken orally or applied topically as a gel or ointment. Another commonly prescribed antibiotic is metronidazole, which has been found to be effective against certain types of bacteria that cause gum disease.
In some cases, dentists may also prescribe amoxicillin or clindamycin as part of the treatment plan for gum disease. These antibiotics work by killing harmful bacteria and reducing infection.
It’s important to note that while antibiotics can be an effective tool in fighting gum disease, they should always be used under the guidance and supervision of a dental professional. Antibiotics alone cannot fully treat gum disease; they should be used in conjunction with other treatments such as scaling and root planing.
Additionally, it’s worth mentioning that not all cases of gum disease require antibiotic treatment. Mild cases can often be managed through improved oral hygiene practices and regular visits to the dentist for professional cleanings.
Understanding the different types of antibiotics used in gum disease treatment is essential for both patients and dental professionals alike. By utilizing these medications appropriately, we can take significant steps toward improving oral health and preventing further complications associated with untreated gum disease.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Antibiotic Treatment for Gum Disease
Antibiotics can be a powerful tool in the fight against gum disease. They work by targeting the bacteria that cause the infection, helping to reduce inflammation and promote healing. One of the main advantages of antibiotic treatment is its ability to reach areas that may be difficult to clean with traditional dental hygiene methods alone. This means that antibiotics can help to clear up stubborn infections and prevent further damage.
Another advantage is that antibiotics are relatively easy to use. They often come in pill or capsule form, making them convenient for patients to take at home. This allows individuals with gum disease to continue their treatment without disrupting their daily routines.
However, there are also some disadvantages associated with antibiotic use for gum disease. One concern is the potential for bacterial resistance. Over time, bacteria can become resistant to certain antibiotics, rendering them less effective in treating infections. It’s important for dentists to carefully select appropriate antibiotics and monitor their patient’s progress during treatment.
Additionally, some people may experience side effects from taking antibiotics, such as nausea or diarrhea. These side effects are usually temporary but can still be uncomfortable or inconvenient.
While antibiotic treatment can offer significant benefits in combating gum disease, it’s essential to weigh these advantages against potential drawbacks like bacterial resistance and side effects. Dentists should evaluate each patient’s unique situation before prescribing antibiotics and consider alternative approaches when appropriate
Precautions and Side Effects of Antibiotic Use for Gum Disease
When it comes to treating gum disease, antibiotics can be a helpful tool. However, it’s important to be aware of the precautions and potential side effects that come with their use.
It’s crucial to take antibiotics exactly as prescribed by your dentist or healthcare professional. Skipping doses or stopping treatment prematurely can lead to ineffective results and even antibiotic resistance.
Additionally, some individuals may experience side effects when taking antibiotics for gum disease. These can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or an upset stomach. If you notice any unusual symptoms while on antibiotics, it’s important to reach out to your dentist or doctor immediately.
Another precautionary measure is avoiding certain foods and beverages while on antibiotic treatment. Some antibiotics interact negatively with alcohol or specific types of food, which could decrease their effectiveness.
Moreover, individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding should exercise caution when considering antibiotic treatment for gum disease. It’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any medication during pregnancy or while nursing.
In rare cases, allergic reactions may occur when using certain types of antibiotics. If you experience difficulty breathing, swelling in the face, lips, tongue, rash, itching, or dizziness after taking an antibiotic for gum disease – seek emergency medical attention right away!
While these precautions and potential side effects should not discourage you from utilizing antibiotics as a part of your gum disease treatment plan if recommended by a professional – they serve as reminders that proper care must be taken throughout the process.
Remember: communication with your dentist is key! They will guide you through each step of the treatment journey and address any concerns that arise along the way.
Natural Alternatives to Antibiotics for Gum Disease
When it comes to treating gum disease, antibiotics are often prescribed by dentists. However, if you’re looking for alternative options or want to try a more natural approach, there are several options worth considering.
1. Oil Pulling: This ancient Ayurvedic technique involves swishing oil (such as coconut or sesame) in your mouth for 10-15 minutes. It is believed to help reduce bacteria and plaque in the oral cavity.
2. Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs like tea tree oil, clove oil, and peppermint have antibacterial properties that can help fight gum disease. These can be used topically or added to homemade mouth rinses.
3. Probiotics: By promoting beneficial bacteria in the mouth, probiotics may help balance the oral microbiome and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria associated with gum disease.
4. Vitamin C: Boosting your intake of vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens can support gum health by strengthening blood vessels and reducing inflammation.
5. Green Tea: Known for its antioxidant properties, green tea has been shown to inhibit bacterial growth in the mouth and reduce inflammation associated with gum disease.
While these natural alternatives may offer some benefits in managing gum disease symptoms, it’s important to remember that they should not replace professional dental care or antibiotic treatment when necessary. Always consult with your dentist before trying any new remedies or supplements.
Importance of Proper Dental Hygiene in Preventing Gum Disease
- Proper dental hygiene is crucial when it comes to preventing gum disease. Maintaining a consistent oral care routine can significantly reduce the risk of developing this common condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
- Regular brushing and flossing are essential in removing plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums. Brushing at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush helps to remove food particles, plaque, and tartar buildup. Flossing once a day reaches areas that your toothbrush can’t, such as between the teeth and along the gumline.
- In addition to brushing and flossing, using an antibacterial mouthwash can further enhance your oral hygiene routine. Mouthwashes containing active ingredients like chlorhexidine or cetylpyridinium chloride help kill bacteria that cause gum disease.
- Visiting your dentist for regular check-ups is another important aspect of maintaining proper dental hygiene. Professional cleanings remove any stubborn tartar buildup that cannot be removed by regular brushing or flossing alone.
- It’s also worth noting that certain lifestyle choices can influence your susceptibility to gum disease. Smoking, for example, weakens the immune system and reduces blood flow to the gums, making them more prone to infection.
- By prioritizing good dental hygiene practices in our daily lives, we take proactive steps toward preventing gum disease from occurring. Remember: prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to our oral health!
Maintaining healthy gums is crucial for overall oral health, and antibiotics can play a role in treating gum disease. However, it’s important to remember that antibiotics are not the sole solution and should be used in conjunction with proper dental hygiene practices.
There are different types of antibiotics used in gum disease treatment, including tetracycline, metronidazole, and amoxicillin. These medications work by targeting and eliminating the bacteria causing the infection.
While antibiotic treatment offers several advantages, such as targeted bacterial eradication and reducing inflammation, there are also disadvantages to consider. Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of beneficial bacteria in the mouth and may lead to resistance if overused or misused.
It’s essential to take precautions when using antibiotics for gum disease. Always follow your dentist’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Be aware of potential side effects like gastrointestinal issues or allergic reactions.
If you prefer natural alternatives to antibiotics for gum disease management, there are options available. Good oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing with a soft toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help prevent gum disease from developing or progressing further.
Remember that prevention is key when it comes to maintaining healthy gums. Regular dental check-ups allow your dentist to detect any signs of gum disease early on before it becomes more severe.
Looking For A Dentist In South Austin, TX
We’re so glad you’re here, and we’d love to welcome you to Daylight Dental Austin ! Featuring preventive care from our friendly team, this exclusive offer has everything you need to get started with us and maintain lifelong oral health. We can’t wait to meet you and your smile soon!