Tooth Extraction Bleeding: Know How To Stop It!
Tooth extraction is a common dental procedure performed for various reasons, including severe decay, infection, crowding, or trauma. While the extraction process itself is relatively straightforward, one of the most common concerns afterward is bleeding. Bleeding after a tooth extraction is normal, but it’s essential to know how to manage it effectively to promote healing and prevent complications.
Understanding Tooth Extraction Bleeding:
Bleeding is a natural part of the body’s healing process. When a tooth is extracted, it leaves behind a socket in the gum tissue where the tooth was anchored. Bleeding occurs as the body responds to this wound by forming a blood clot to protect the exposed area and initiate tissue repair.
In most cases, bleeding after a tooth extraction is minor and should gradually decrease within a few hours after the procedure. However, some factors can contribute to increased bleeding or difficulty in controlling it. These factors include:
- Blood-thinning medications: If you are taking blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants) such as aspirin, warfarin, or clopidogrel, you may experience prolonged bleeding after a tooth extraction.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hemophilia or liver disease, can impair the body’s ability to form blood clots, leading to excessive bleeding.
- Smoking: Smoking can constrict blood vessels and impair blood flow, which may delay the formation of a blood clot and increase the risk of bleeding after a tooth extraction.
- Trauma during extraction: If the tooth extraction involves significant trauma to the surrounding tissues, it may result in more extensive bleeding.
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene can increase the risk of infection, which may interfere with the healing process and lead to prolonged bleeding.
How to Stop Tooth Extraction Bleeding:
If you experience bleeding after a tooth extraction, there are several steps you can take to help stop it and promote healing:
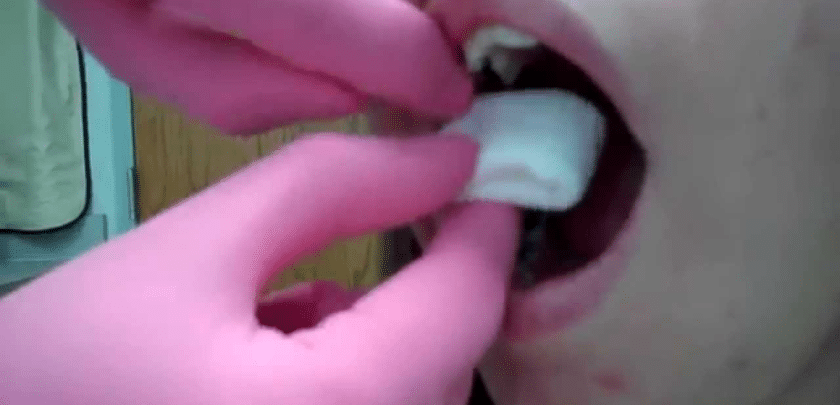
- Bite on gauze: Immediately after the tooth extraction, your dentist or oral surgeon will place a piece of gauze over the extraction site and instruct you to bite down firmly on it. This pressure helps promote the formation of a blood clot. Keep the gauze in place for the recommended amount of time, usually around 30 minutes to an hour.
- Avoid spitting or rinsing: Avoid spitting, rinsing your mouth vigorously, or using a straw during the first 24 hours after the extraction. These actions can dislodge the blood clot and lead to increased bleeding.
- Apply pressure: If bleeding persists after removing the initial gauze, you can place a fresh piece of gauze over the extraction site and apply firm pressure by biting down on it for another 30 minutes to an hour.
- Use a tea bag: If bleeding continues despite applying pressure with gauze, try placing a moistened tea bag (preferably black tea) over the extraction site and biting down on it. Tea contains tannins, which can help promote blood clotting and reduce bleeding.
- Elevate your head: Keeping your head elevated with an extra pillow while resting can help reduce blood flow to the extraction site and minimize bleeding.
- Avoid strenuous activities: Avoid engaging in strenuous activities or heavy lifting for at least 24 hours after the tooth extraction, as these activities can increase blood pressure and exacerbate bleeding.
- Ice pack: Applying an ice pack to the outside of your cheek near the extraction site can help constrict blood vessels and reduce bleeding and swelling.
- Avoid smoking: If you smoke, refrain from smoking for at least 24 hours after the tooth extraction, as smoking can impair healing and increase the risk of bleeding and complications.
When to Seek Professional Help:
In most cases, bleeding after a tooth extraction will gradually decrease and stop within a few hours. However, if you experience persistent or excessive bleeding, it’s essential to seek prompt medical attention. Contact your dentist or oral surgeon if:
- Bleeding persists for more than 24 hours after the extraction.
- You experience severe bleeding that fills your mouth with blood or requires frequent gauze changes.
- You develop signs of infection, such as increasing pain, swelling, redness, or foul odor or taste in your mouth.
- You have a medical condition or take medications that may affect blood clotting, and you’re concerned about excessive bleeding.
- You have other symptoms of complications, such as fever, nausea, vomiting, or difficulty breathing.
Your dentist or oral surgeon will evaluate your condition and may recommend additional measures to control the bleeding, such as applying a topical hemostatic agent or suturing the extraction site. In rare cases of severe or uncontrollable bleeding, you may need to be referred to a hospital for further evaluation and treatment.
Preventing Complications:
While bleeding after a tooth extraction is normal, it’s essential to take precautions to prevent complications and promote optimal healing. Follow your dentist’s post-extraction instructions carefully, which may include:
- Avoid vigorous rinsing or spitting for the first 24 hours.
- Eating soft foods and avoiding hard, crunchy, or spicy foods that may irritate the extraction site.
- Taking prescribed medications, such as pain relievers or antibiotics, as directed.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene by gently brushing and flossing around the extraction site, being careful to avoid the area itself.
- Attending follow-up appointments with your dentist or oral surgeon for evaluation and removal of any sutures if necessary.
By following these guidelines and knowing how to effectively manage bleeding after a tooth extraction, you can promote healing and reduce the risk of complications. If you have any concerns or questions about your recovery process, don’t hesitate to contact your dental provider for guidance and support.